SaaS, or Software as a Service, is a model that has revolutionized how companies access and use software, moving away from traditional purchase and installation to a more flexible, subscription-based approach.
Whether you’re a newcomer eager to grasp the basics or a seasoned professional seeking to refine your approach, this guide will walk you through the essentials of SaaS sales.
We’ll break down SaaS sales in detail, shedding light on its definition, significance, and the many ways it can catapult your business to new heights.
Ready to transform your sales results? Let’s get started!
What is SaaS Sales?
SaaS sales is the process of selling software that is hosted in the cloud and accessed over the internet, typically through a subscription model rather than a one-time purchase.
It allows customers to use software applications without the need for complex installations or maintaining hardware.
Selling SaaS requires a deep understanding of the customer’s business needs and a commitment to providing a solution that evolves with those needs over time.
Common types of SaaS products include:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems: These integrate core business processes, such as inventory management, accounting, human resources, and more, into a single system.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software: Businesses can use these to manage and analyze customer interactions and data.
- Project management systems: These systems offer tools to help businesses plan, execute, and monitor projects.
- Accounting software: Accounting software automates financial functions and transactions, simplifying financial management, reporting, and compliance.
- Marketing automation platforms: These platforms automate marketing tasks, such as email campaigns and social media posting, to improve efficiency and personalize customer engagement.
- Productivity software: With these, businesses can enhance efficiency in individual and collaborative tasks.
Overall, the goal of SaaS sales is to build a recurring revenue stream by offering compelling, constantly evolving software services that drive customer success and loyalty.
Why is Focusing on SaaS Sales Important?
SaaS plays a pivotal role in driving revenue growth, fostering customer relationships, and ensuring long-term business sustainability.
Here are some reasons why selling SaaS products is important for businesses:
- Recurring revenue streams: Subscription models provide businesses with a steady, predictable flow of income, enabling better financial planning and stability.
- Lower entry costs for customers: SaaS removes the barrier of high initial costs for customers, making cutting-edge software solutions accessible to a broader audience.
- Rapid deployment & scalability: The cloud-based nature of SaaS allows for quick deployment and easy scalability, catering to businesses of all sizes and their changing needs.
- Enhanced customer relationships: The ongoing subscription model fosters closer relationships with customers, providing continuous engagement and opportunities to deliver value.
- Global reach: SaaS eliminates geographical limitations by allowing businesses to serve customers worldwide with minimal increase in cost.
- Data insights and performance metrics: SaaS sales provide invaluable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and usage patterns. By leveraging these analytics, sales teams can gain a deeper understanding of their target audience, identify trends, and personalize their approach to maximize conversion rates and customer retention.
3 Types of SaaS Sales Models
In this section, we’ll explain three common types of SaaS sales models. Understanding these models is crucial for tailoring your approach to fit your product offerings and customer needs.
1. Self-service model
In the self-service model, customers can sign up, subscribe, and start using software directly from the company’s website, often with minimal interaction with its sales team.
This model is designed for simplicity and ease of use, as it caters primarily to individual users or small businesses that prefer a hands-off approach.
It relies heavily on an intuitive UI/UX and compelling marketing strategies to guide the customer through the purchasing process.
Note: This model is particularly effective for SaaS products with relatively low pricing.
2. Transactional sales model
When customers consider spending more money on a product, they often want to interact with the company first. This is because they see more risk in making a bigger purchase, especially if the price is higher.
This is why sales teams play a significant role in this model, as they help to build relationships with potential clients and turn them into customers.
In essence, the transactional sales model is characterized by efficient, high-volume sales and support operations, short sales cycles, and rapid onboarding (supported by automation that allows for as much customer self-service as possible.)
Note: Since sales reps need to properly engage with potential customers, they often have some autonomy in this model — they can offer demos & discounts, answer questions, and guide customers towards tiered pricing models to facilitate the buying decision.
3. Enterprise sales model
The enterprise sales model is geared towards selling high-value SaaS solutions to large organizations.
It involves lengthy sales cycles, as it requires detailed sales demonstrations, customization, and negotiation to fit the large-scale needs of enterprise clients.
So, to effectively navigate these complex sales processes, enterprise SaaS sales reps must possess in-depth technical knowledge of the product.
They’ll also need to engage deeply with potential clients to understand their unique challenges and tailor solutions accordingly.
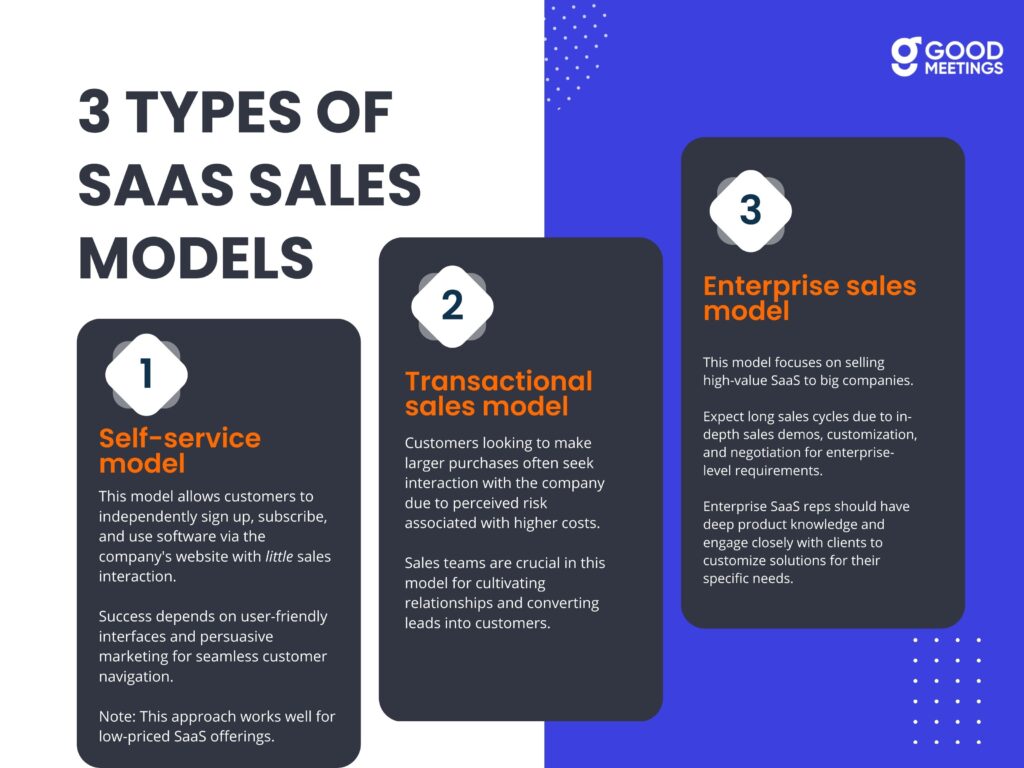
Image Source: Goodmeetings
Picking the Right SaaS Sales Model For Your Business
Choosing the appropriate SaaS sales model for your business is a key decision that can significantly impact your growth, customer satisfaction, and revenue.
Let’s explore some important considerations and steps that will guide you in selecting the most suitable SaaS sales model for your business:
1. Understand your target audience
Begin by deeply understanding who your customers are, their buying behaviors, and their preferences.
Are they small businesses that prefer a straightforward, self-service model? Or are they large enterprises in need of customized solutions and a high-touch sales approach?
The nature and needs of your target audience will heavily influence your choice of sales model.
2. Evaluate your product complexity
Next, you need to assess how complex your SaaS product is.
Simple, intuitive products that offer clear value might be well-suited to a self-service or transactional sales model.
In contrast, complex solutions requiring integration or customization are better served by an enterprise sales model.
3. Assess your sales resources and capabilities
Evaluate your company’s resources in terms of sales personnel, marketing budget, and customer support.
For instance, a resource-intensive model like the enterprise sales model requires a skilled sales force capable of managing long sales cycles and complex negotiations.
If your resources are limited, starting with a less resource-intensive model and gradually expanding as you grow could be more practical.
4. Consider your growth and scaling goals
Think about how each sales model aligns with your ambitions for scaling and growth. The self-service and transactional models can offer faster scaling with lower customer acquisition costs, suitable for rapid expansion.
On the flip side, the enterprise sales model, while slower and more resource-intensive, can lead to significant contracts and deeper market penetration over time.
5. Factor in your business positioning and needs
Every business has its unique positioning and set of needs, influenced by factors such as market presence, brand perception, and strategic objectives.
Recognizing where your business stands—and where it aims to go—enables you to tailor your sales model to support these goals effectively.
Aligning your sales model with your business positioning ensures coherence between your sales strategies and broader business ambitions.
Understanding the Stages of the SaaS Sales Process
The SaaS sales process encompasses several stages, each crucial for converting prospects into loyal customers.
Here’s a breakdown of this process:
1. Creating detailed customer personas
The foundation of an effective SaaS sales strategy starts with a deep understanding of your target customer.
Creating detailed customer personas involves researching and compiling the characteristics, pain points, motivations, and behavior patterns of your ideal customers.
This step ensures your sales and marketing efforts resonate with the needs and desires of your target audience.
2. Prospecting
Prospecting involves identifying potential customers (leads) who fit your customer persona and are likely to benefit from your SaaS solution.
This involves a mix of strategies, including inbound marketing, content marketing, social media engagement, and outbound approaches like cold emailing and calling.
The goal here is to create a pool of prospects that can be further nurtured and converted into paying customers.
Related: 10 B2B Sales Prospecting Tools in the Market
3. Qualifying
Remember: not all leads are created equal. Qualifying leads means assessing whether they have a genuine need for your product, the budget to purchase it, and the authority to make buying decisions.
It ensures that your sales efforts are concentrated on leads that are most likely to convert, optimizing resources and increasing the chances of success.
4. Presenting the product
Once a lead is qualified, the next step is to present your SaaS product.
It’s not just about showcasing the features of your SaaS product; it’s about telling a compelling story that resonates with the prospects’ needs and challenges.
This stage is your opportunity to make a lasting impression, to demonstrate not only what your product does but how it can transform the way a business operates.
Related: Mastering Sales Demos: The Ultimate Guide to Winning & Closing More Deals
5. Handling objections
Objections are a natural part of the sales process.
Whether it’s concerns about cost, implementation, or compatibility with existing systems, handling objections with confidence and clarity is important.
This involves listening carefully to the prospect’s concerns, providing them with informative and reassuring responses, and demonstrating flexibility where possible to accommodate their needs.
Here’s a simple guide that explains more about objection handling.
6. Closing the deal
This critical phase involves negotiating terms, discussing pricing, and ultimately getting the prospect to commit to your product.
However, it often proves to be the most challenging, as it requires a delicate balance of persuasion, negotiation, and relationship-building.
Closing isn’t just about getting the prospect to sign on the dotted line; it’s about reinforcing the value proposition, addressing last-minute concerns, and ensuring that the decision to purchase feels like the start of a valuable partnership.
7. Nurturing the customers
Your business relationship with a customer shouldn’t end with a closed deal.
Nurturing involves ongoing engagement to ensure customer satisfaction, encourage loyalty, foster long-term relationships, and even generate referrals.
This can include regular check-ins, providing helpful resources, addressing any issues promptly, and identifying opportunities for upselling or cross-selling.
Related: What is Sales Acceleration? – Tools and Tactics Included
10 SaaS Sales Metrics That You Should Keep an Eye on
If you want to assess the health and performance of your SaaS sales efforts, as well as identify areas for improvement, there are some important metrics you should track.
Let’s take a look at them:
1. Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
This represents the amount of revenue generated from your active subscriptions each month.
Tracking MRR provides insight into your financial health and growth trajectory, helping you gauge whether your sales strategies are effectively translating into steady revenue streams.
Formula = Total number of monthly subscribers x the average revenue per user (ARPU).
2. Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)
ARR is used to measure the total amount of recurring revenue expected from recurring subscriptions in a year.
Formula = MRR x 12
3. Net Revenue Retention Rate (NRR)
NRR measures the revenue retained from existing customers over a specific period. It accounts for upgrades, downgrades, and churn.
This metric is a powerful indicator of customer satisfaction and the effectiveness of your upsell and cross-sell strategies.
A high NRR signifies that not only are you retaining customers, but you’re also successfully increasing their value over time.
Formula = (Starting MRR + Expansion Revenue – Churned Revenue) ÷ Starting MRR x 100
4. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
This is used to gauge customer loyalty and satisfaction by measuring the likelihood of customers recommending a company’s product or service to others.
It provides insights into overall customer sentiment and helps businesses understand the strength of their customer relationships.
The NPS survey typically consists of a single question: “On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our product/service to a friend or colleague?” Based on their responses, customers are categorized into three groups:
- Promoters (score 9-10): These are customers who are highly satisfied with the product or service and are likely to recommend it to others.
- Passives (score 7-8): Passives are customers who are satisfied with the product or service but may not actively promote it to others.
- Detractors (score 0-6): Detractors are customers who are dissatisfied with the product or service and may spread negative feedback or even discourage others from using it.
Formula = % of Promoters – % of Detractors
5. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
CAC measures the total cost of acquiring a new customer, including all marketing and sales expenses.
Understanding your CAC is crucial for evaluating the efficiency of your marketing strategies and ensuring that the cost to acquire a customer does not exceed the revenue they bring in.
Formula = Total Sales and Marketing Expenses ÷ Number of New Customers Acquired
Typically, you should aim for a CAC that’s significantly lower than the Lifetime Value (LTV) of a customer.
6. Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)
CLTV represents the total revenue that a customer is expected to generate throughout their entire relationship with a company.
It helps businesses understand the long-term value of investing in customer relationships and optimizing sales strategies to increase this value over time.
Formula = Customer Value x Average Customer Lifespan
7. Churn Rate
This measures the percentage of customers who cancel or do not renew their subscriptions within a given period.
It’s a direct reflection of customer satisfaction and product-market fit. A high churn rate may signal underlying issues with the product, service, or customer experience that need immediate attention.
Formula =Customers at the Beginning of Period – Customers at the End of Period ÷ Customers at the Beginning of Period x 100
8. Win Rate
The win rate is a metric that measures the percentage of deals won compared to the total number of opportunities pursued within a specific period.
A high win rate indicates that a sales team is effectively converting a significant portion of their opportunities into closed deals.
Formula = (Number of Deals Won ÷ Total Number of Opportunities) x 100
Related: 6 Proven Ways To Close More Deals
9. Sales Qualified Leads
Sales Qualified Leads (SQLs) are prospective customers who have been evaluated and determined to have a high likelihood of becoming paying customers based on their interactions with the sales team.
Tracking SQLs helps in assessing the quality of leads generated and the effectiveness of lead qualification processes.
10. Lead Velocity Rate (LVR)
This measures the month-over-month growth in qualified leads, providing insights into the future revenue and growth potential.
It’s a leading indicator of sales performance, as it reflects the health of your sales pipeline.
Formula = (Number of Qualified Leads This Month – Number of Qualified Leads Last Month) ÷ Number of Qualified Leads Last Month x 100
6 Challenges of Selling SaaS Products
Navigating SaaS sales comes with its unique set of challenges.
Despite the numerous advantages and opportunities this business model offers, SaaS companies often encounter hurdles that can impede growth, customer acquisition, and retention.
Here are some of them:
1. Customer churn
Retaining customers can be as challenging as acquiring new ones, especially if the product fails to meet evolving customer expectations or if competitors offer more attractive alternatives.
Strategies to overcome: Implementing a robust customer success program that actively engages users and addresses their concerns can enhance satisfaction and loyalty. Regularly updating the product based on customer feedback and market trends can also help retain customers.
2. Differentiating from competitors
The SaaS market is highly competitive, with numerous players offering similar solutions. Standing out in a crowded marketplace and differentiating your product from competitors can be a significant challenge.
Strategies to overcome: Focusing on niche markets or specific pain points can help create a more targeted and compelling offering. Building a strong brand and customer experience can also differentiate your product from competitors.
3. Choosing the right pricing model
Determining the appropriate pricing model for your SaaS product can be tricky. You need to balance affordability for customers while ensuring sustainable revenue for your business.
Strategies to overcome: Experiment with different pricing structures and continuously gather feedback. You can also consider offering multiple tiers to cater to different customer segments.
4. Wasting time on unqualified leads
Pursuing leads that are unlikely to convert can drain resources and prevent you from focusing on more promising prospects.
Strategies to overcome: Improving lead qualification processes and employing scoring systems can help identify high-potential leads early on. Training your sales team to recognize and prioritize these leads can optimize sales efforts and improve conversion rates.
Related: The art of knowing when to walk away from a deal
5. Aligning sales and marketing teams
A common hurdle in SaaS selling is ensuring the sales and marketing teams work in tandem towards shared goals, rather than in silos. Misalignment can lead to inconsistent messaging and wasted opportunities.
Strategies to overcome: Implementing shared goals and metrics can foster alignment. Regular cross-departmental meetings and communication channels can ensure everyone is on the same page.
Related: 10 Critical Sales Communication Skills For Success in 2024
6. Converting free users to paying ones
Many SaaS businesses offer free trials or versions to attract users, but converting these users into paying customers can be challenging, especially if the value proposition is not clear or compelling enough.
Strategies to overcome: Enhancing the onboarding process to immediately showcase the value of your product can improve conversion rates. Plus, providing timely, personalized follow-ups and exclusive offers can encourage free users to upgrade.
Top SaaS Sales Best Practices
Now, let’s explore some SaaS sales best practices that can help you enhance customer experiences and drive sustainable growth.
1. Employ effective SaaS sales techniques
Implementing certain techniques in your SaaS sales strategy can help you convert leads into loyal customers:
- Have comprehensive product knowledge: A deep understanding of your product’s features, benefits, and applications allows you to address customer questions confidently and highlight how your solution meets their specific needs.
- Identify upsell and cross-sell opportunities: Regularly review customer usage and feedback to identify potential upsell or cross-sell opportunities.
- Call prospects as soon as they sign up: Immediate follow-up calls to new sign-ups demonstrate your commitment to customer service and provide a personal touch.
- Use automated email campaigns: These will keep your prospects engaged by providing them with valuable information, updates, and reminders about your product, gradually nudging them through the sales funnel.
2. Use the right tools
Leveraging the right sales tools can greatly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your SaaS sales process.
For instance, an AI-powered platform like Goodmeetings provides tons of helpful features that will enhance your team’s productivity and help them close deals faster.
Let’s check out some of these features:
- Offers AI-powered call recording, transcriptions, and summaries so you can easily capture and revisit critical moments from customer interactions.
- Provides AI-based & human coaching to help you train your reps and ultimately build a high-performing SaaS sales team.
- Gives you a complete picture of customers with detailed profiles (including their names, designation, and previous interactions) so your reps can personalize their pitches.
- Lets you create questionnaires that you can use to generate and qualify leads based on responses. This ensures that your team’s sales efforts are focused where they’re most likely to convert.
- Streamlines your sales workflow by providing automated action items & deep CRM integrations.
- Allows you to measure the effectiveness of your team’s sales presentations with actionable insights.
Want to get started with Goodmeetings? You can book a free demo today (no credit required!)
3. Optimize the free trial experience
Free trials are a common strategy in SaaS to attract new users by allowing them to experience the product firsthand. So, enhancing this experience is crucial for converting trial users into paying customers.
You can do so by ensuring that the onboarding process is smooth, offering guidance and resources to help users get the most out of their trial, and providing timely support to address any issues or questions.
4. Focus on value, not features
While it may be tempting to tout every feature of your SaaS product, focusing on value is what truly resonates with buyers.
Customers are interested in how your solution can solve their problems or improve their operations, not necessarily in the technical specifics.
Frame your sales conversations around the tangible benefits and outcomes that customers can expect, and how your product uniquely delivers on those fronts.
Improve Your SaaS Sales Pitch Using GoodMeetings
In conclusion, it’s clear that success in SaaS sales requires more than just a great product; it demands a strategic approach to sales, a deep understanding of customer needs, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Plus, by integrating a tool like Goodmeetings into your sales process, you can transform your sales presentations into engaging, interactive experiences that capture and hold your prospects’ attention!
GET IN TOUCH



![15 Best AI Sales Tools & Software [2024]](https://goodmeetings.ai/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/THE-ULTIMATE-GUIDE-TO-WINNING-CLOSING-MORE-DEALS-2-1024x536.png)
